| Design Assistance Step 4 : Select a Glass Type |
| Need Assistance? | ||||||
| Call us Toll Free (U.S.) | ||||||
| 1-866-624-ESKY (3579) | email: info@e-skylight.com | |
| A. | Float Glass: ASTM C 1036.
| |
| B. | Heat Treated Glass: ASTM C1048, with surface stress of 5000psi, +/- 1500psi.
| |
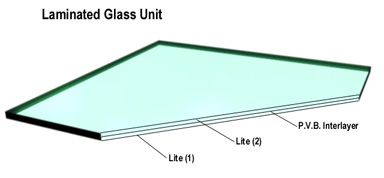
| C. | Laminated Glass: Two lites of equal thickness bonded with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, meeting criteria of ANSI Z97.1-1984 and CPSC 16 CFR 1201 for safety glazing. | |
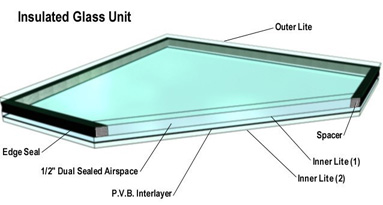
| D. | Insulating Glass: CBA rated by the Insulating Glass Certification Council when tested in accordance with ASTM E 773 and E 774. Dual edge seals with silicone secondary seal. Exterior lite is to be heat strengthened; interior lite to be laminated glass. |
| A. | Probability of breakage not to exceed 8/1000 for vertical glass and 1/1000 for sloped glass upon first application of design pressures or due to anticipated thermal stresses. |
| A. | Laminated Glass: two ¼" clear, heat strengthened lites with a (.030) (.060) polyvinyl butyral (P.V.B.) interlayer.
| |
| B. | Insulated laminated glass consisting of a ¼" clear heat strengthened lite, a ½" dual sealed airspace over a laminated lite (thickness to be determined per glass size) with a (.030) (.060) polyvinyl butyral (P.V.B.) interlayer. | |
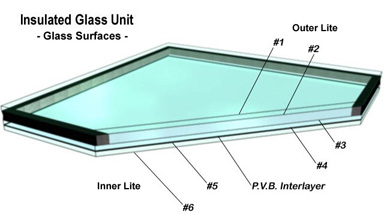
| C. | Insulated laminated glass consisting of a ¼" clear heat strengthened lite, a ½" dual sealed airspace over a laminated lite (thickness to be determined per glass size) with a (.030) (.060) polyvinyl butyral (P.V.B) interlayer. A LOF Energy Advantage pyrolytic low-e coating is applied to surface #2 (Coating will be applied to surface #3 with tinted glass). | |
| D. | Insulated laminated glass consisting of a ¼" clear heat strengthened lite, a ½" dual sealed airspace over a laminated lite (thickness to be determined per glass size) with a (.030) (.060) polyvinyl butyral (P.V.B.) interlayer. A PPG Solarban 60 low-e coating is applied to surface #2. |

| Visible Light Transmittance: | The percentage of visible light that is transmitted through the glass. Interior daylight levels will be determined by this value. The higher the percentage, the more daylight is transmitted. |
| Solar Transmittance: | The percentage of ultraviolet, visible and near infrared energy that is transmitted through the glass. |
| Visible Light Reflectance: | The percentage of light that is reflected from the glass surface. |
| Solar Reflectance: | The percentage of solar energy that is reflected from the glass surface. |
| ASHRAE U-Value: | The amount of heat gain or loss through glass due to the difference between indoor and outdoor temperatures (based upon ASHRAE standard winter nighttime and summer daytime conditions). The colder the climate, and the more expensive the heating fuel, the more important it is to utilize a low U-value glass. |
| Shading Coefficient: | The ratio of solar heat gain through a specific type of glass product to the solar heat gain of a 1/8" (3mm) clear glass. The lower the shading coefficient number, the better the performance of the glass. This is particularly important in warmer climates. |
| Relative Heat Gain: | The amount of heat gain relative to the effects of the solar heat gain (shading coefficient) and conductive heat gain (U-Value) of the glass. The lower the relative heat gain value, the more efficient the glass is in restricting heat gain. |
Product |
Transmittance |
Reflectance |
ASHRAE U-Value |
Shading Coefficient |
Solar Heat Gain Coefficient |
Relative Heat Gain |
||||
Visible |
Solar |
Vis-In | Vis-out | Solar | Summer |
Winter |
||||
| Clear Insulated Laminated w/ PPG Solarban 60 | 69% | 32% | 12% | 12% | 28% | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.44 | 0.37 | 92.06 |
| Clear Insulated Laminated w/ Pyrolytic Low-e | 69% | 46% | 15% | 18% | 13% | 0.38 | 0.34 | 0.76 | 0.65 | 158 |
| Clear Insulated Laminated | 77% | 53% | 14% | 14% | 11% | 0.56 | 0.47 | 0.78 | 0.67 | 163 |
| Clear Laminated | 87% | 68% | 7% | 7% | 6% | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.86 | 0.74 | 187 |